DAS Networks
DAS And Small Cell Network Management
Since 2004, Steel in the Air has helped over 4,300 private landowners, commercial property owners, municipal governments, and other public entities (universities, public utilities, parks and churches) understand and favorably position themselves in cellular lease negotiations and small cell infrastructure deployment. We take pride in providing our clients with the best advice in consideration of all possible factors. Whether you seek to deploy a DAS or small cell solution yourself or have been contacted by a company who wants to use your property to install one, we can be of assistance.

Here’s What We Can Help You To Do:
Understand Your Options
Contact Us
Choose The Right Partner
Achieve Value
About DAS Systems
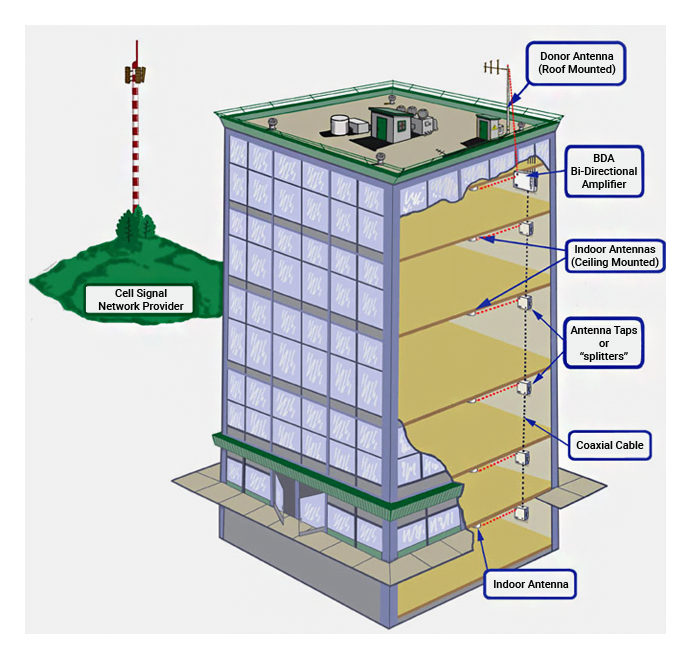
A Distributed Antenna System (DAS) is an antenna infrastructure used to improve the service of one or more Wireless Service Provider (WSP) within a defined coverage area. This coverage area can be either an indoor venue (e.g., office building, stadium, or airport) or an outdoor environment (e.g., college campus, metropolitan area). Unlike a traditional cell site which has antennas mounted on a single tower or building, a DAS uses several antennas spread across the target coverage area. This coverage area is determined by a WSP based on their need to improve signal quality or system capacity.
There are two key components to any DAS, the signal source and the distribution system. The selections made for each of these components determine the level of service provided.
DAS Signal Source
- Bi-Directional Amplifier (BDA)-operates by amplifying and retransmitting the existing outdoor signal. A BDA uses an outdoor antenna, typically mounted on the rooftop, to bring the outdoor signal in to the building. This signal is amplified and fed into the distribution system.
- Base Transceiver Station (BTS)-this is the same radio that is used at a cell site and provides both coverage improvement and additional capacity to the venue. A BTS is typically installed in the main IT room of a building and connects to the WSP network via T1 or other Ethernet connection. The output of the BTS is routed into the distribution system.
DAS Distribution System
The DAS distribution system transports the signal from the source to the users located throughout the venue. The type of distribution used is determined by the size of the venue and the level of service required. There are two main types of distribution systems which are used in typical DAS systems:
Passive DAS-is a network of coaxial cable, power dividers and antennas. Due to the glossy nature of coaxial cable, this type of DAS is typically used only in smaller facilities.
Active DAS-converts the radio frequency (RF) signal to another format to transport throughout the venue.
There are several components to an active DAS:
- Main Hub – converts the RF signal to another format (e.g., fiber optic or Ethernet)
- Distribution Medium – fiber optic or Ethernet cable is used to transport the signal to the remote equipment which is typically located telco or IDF closets. The distribution medium can often use existing cable in the facility.
- Remote Equipment – converts the signal back to RF and connects to antennas via coaxial cable.
- Antennas – are located throughout the venue. The number of antennas required depends on the size of the venue and the quality of service required.
Which Solution Is Best?
There is no direct answer to this question. The right DAS solution depends largely on the coverage requirements of the DAS and the unique characteristics of the venue to be covered. The answer can also be biased by the individual interests of the parties involved. Only an expert advisor can ensure that you get the right DAS for your building. If you think you need a DAS in your building or have been contacted by a WSP who would like to install one please don’t hesitate to contact us.

Insider tips
- While small cell and DAS deployment won’t decrease the need for towers in rural areas, we believe the trend in the next 10 years will, in fact, lean towards small cell deployment.
- Wireless carriers may eventually seek to reduce their dependence on cell tower leases that have high lease rates by replacing them with small cell technologies.