Types of Cell Towers
Cell Phone Tower Types And Information
Cell phone towers are structures built on specific parcels of land that are designed to accommodate wireless tenants. Wireless tenants utilize cell towers to deploy various technologies to a subscriber base, such as telephony, mobile data, television and radio. Cell towers are typically built by tower companies or wireless carriers.
We receive many inquiries from property owners who confuse the actual tower with antennas that are placed on rooftops. These antennas are more accurately described as cell “sites”, but the real definition of a cell site is an area within a wireless service providers network that can be serviced by an antenna array. Thus, there can be multiple cell sites (and multiple tenants) on any one given tower (or rooftop). This article will help clarify the difference between the types of towers and the equipment that is placed on and used for cell site transmissions.
Five Main Types Of Towers

The Monopole Tower
Contact Us

The Lattice Tower
The Lattice Tower is sometimes referred to as “self-support” or SST because it is free-standing. It stands 200-400 ft. tall with a triangular base and three-four sides. It is typically used for telephony. The Eiffel Tower is a lattice tower.

The Guyed Tower

Concealed and Stealth® Towers
Concealed and Stealth® Towers. Stealth ® towers are a particular brand of concealed towers. Another manufacture of concealed towers in Larson Camouflage. Concealed towers are deployed to satisfy zoning regulations and can range in size to accommodate their surroundings. They are more expensive than other types of towers because they require additional material to create a “concealed appearance,” yet at the same time, they provide less capacity to tenants than other towers do. This is one of the more interesting concealed towers, located at a church in California.

Broadcast Towers
Broadcast Towers provide mounting space for FM radio, AM radio, and Television (TV) antennas. Their antennas are massive, weighing anywhere from 1,000 pounds to 15 tons depending upon the type of service they provide and the coverage they are purposed to deploy. Most broadcast towers are guyed towers with three or more guy wires attached to grounded anchors. Broadcast towers can take up a great deal of ground space – up to 300 acres, which is why they are typically found in rural areas or on mountaintops where natural elevation provides the best means of transmitting signals.
Other Equipment

Antenna Array
An Antenna Array is a platform where tenants mount antennas, which signal transmission and reception to mobile devices within a specific area. The number of antennas (typically between 3-18) is based on several factors, including the number of tenants (wireless carriers); the type (voice or data) and volume of transmission; the technology being used (eg: CDMA, GSM, LTE, WiMAX) and the frequency of spectrum (in MgH) utilized.
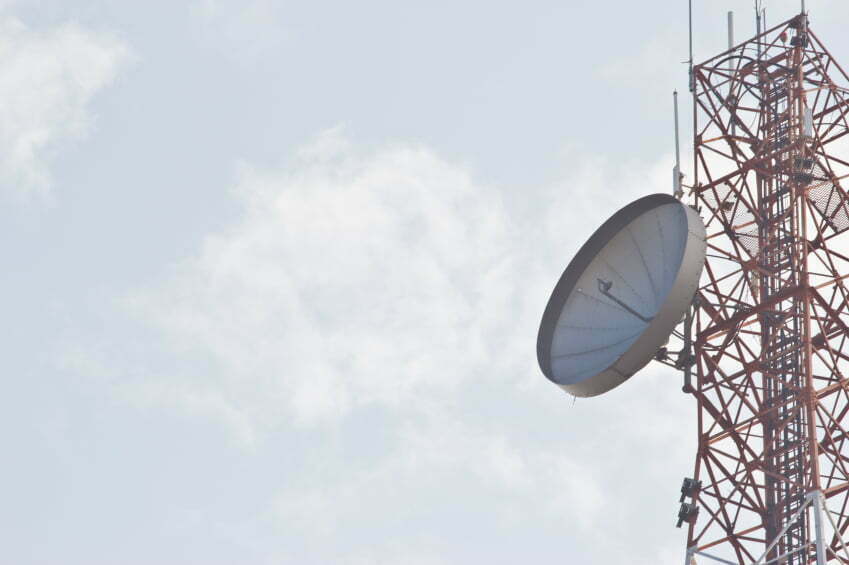

Microwave Dish
The Microwave Dish is a large round antenna, which is used for a specific type of transmission, and also commonly used for backhaul.

Ground Space
The Ground Space is the area that wireless carriers lease from property owners, upon which they build cell towers, cell sites and place shelters, generators and additional equipment.
The Generator is powered by gas or diesel and used as emergency back-up to keep cell sites operational during power outages.

Base Transmitter Station
The Base Transmitter Station is a large round antenna, which is used for a specific type of transmission, and also commonly used for backhaul.
Utilities are also necessary for the operation of cell sites. Wireless carriers will run lines or cables to the site to complement their specific technology.
You may be interested in browsing SITA’s Knowledge Base of informative articles, such as: Cell Tower Zoning and Permit Requests, DAS and WiFi Contracts for Venue Owners, Renegotiating Cell Site Leases, About Lease Optimization Companies, or more.